Many farmers and ordinary people do not know what microbial fertilizers are? How useful is it? I don't know which type of composite microbial bacteria is suitable for me. Based on more than 3000 organic fertilizer and microbial organic fertilizer factories in China, I provide the following detailed introduction. Deep and excellent articles are recommended for collection!
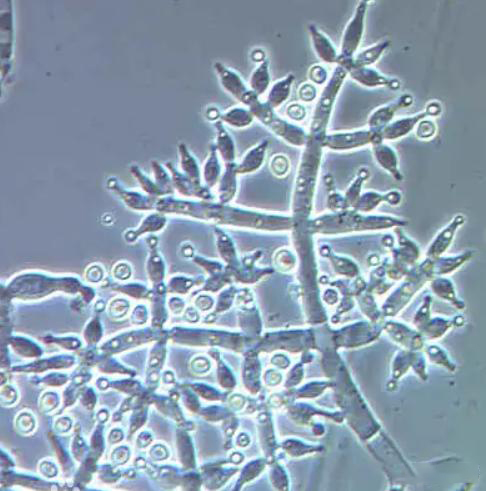
bacillus subtilis
1. Special bacterial cells are treated with spore promotion and microencapsulation, which have good stability in spore state, resistance to oxidation, compression, and high temperature, and can withstand high temperatures of 60 ℃ for a long time. They can survive for 20 minutes at 120 ℃; Acid and alkali resistant, can maintain activity in acidic environments, and can withstand attacks from saliva and bile.
2. After entering the soil in spore form, Bacillus subtilis quickly resurrects from its dormant state and reproduces into a high bacterial population in a short period of time, consuming a large amount of oxygen in the soil and producing hydrogen peroxide and bacteriocins, establishing a microecological balance, promoting the growth of beneficial anaerobic microorganisms, and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria (Escherichia coli, Salmonella).
3. During rapid reproduction, a large amount of various vitamins, organic acids, amino acids, proteases (especially alkaline proteases), saccharifying enzymes, lipases, and amylase are produced, which can degrade complex organic matter in the soil, promote crop absorption, and improve fertilizer utilization efficiency.
4. Safe and efficient, with no drug residues or toxic side effects, it can reduce the use of antibacterial pesticides and enhance plant immunity.
5. It has a good control effect on soil borne diseases such as wilting, root rot, potato late blight, banana Panama disease, etc. in fruit trees, melons, eggplants, ginger, potatoes, yam, Panax notoginseng, ginseng and other crops. The variant methylotrophic Bacillus has a good control effect on various soil borne diseases, especially powdery mildew, root rot, and replanting.
Bacillus subtilis with lateral spores
Promote root growth, sterilize, and degrade heavy metals
1. Bacillus subtilis can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in plant roots, inhibit the reproduction of pathogenic bacteria, promote root growth, enhance root absorption capacity, and activate soil nutrients (nitrogen fixation, phosphorus and potassium solubilization), improve crop yield and quality.
2. Due to the high tolerance, salt tolerance, and acid alkali resistance of Bacillus subtilis, the drying temperature during fertilizer production can reach 260 ℃, which can increase yield and reduce moisture content, making it suitable for industrial production (under the same conditions as producing compound fertilizers). The use of Bacillus subtilis to produce compound fertilizers can provide up to 30% inorganic nutrients and reduce nitrogen fertilizer application.
3. Its disease resistance is very strong, especially for fungal diseases and nematode diseases. It is known as the 'Anti Repetitive Diamond'.
4. The decay rate of the bacterial strain is less than 20% within 12 months.
Gelatinous Bacillus subtilis
Dissolve potassium and release soluble phosphorus, potassium elements, as well as trace elements such as calcium, sulfur, magnesium, iron, zinc, molybdenum, manganese, etc
1. It can promote the dissolution of phosphate and potassium ions, facilitate the transformation of mineral elements from insoluble to soluble states, and enrich the available phosphorus and potassium in the soil.
2. As a plant root and microorganism, it can produce bioactive substances such as auxin and cytokinin to stimulate plant growth.
3. It can produce antibiotic substances, effectively reduce crop diseases, and Bacillus subtilis forms a dominant bacterial community in the rhizosphere of crops, which can inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
4. Generate a large amount of extracellular polysaccharides, promote the formation of soil aggregates, improve soil texture, and enhance soil quality.
5. The bio potassium fertilizer mainly composed of gelatinous Bacillus subtilis has shown good yield increasing effects on various crops in potassium deficient soil. At the same time, it also has a certain nitrogen fixation effect.
Organic fertilizer trough type flipping machine
Paenibacillus polymyxa
1. Has good control effect on soil borne diseases such as bacterial and fungal diseases;
2. Has a good growth promoting effect on plants.
3. Bacillus polymyxoides has a good control effect on bacterial soil borne disease plant bacterial wilt. In the late harvest, the field control effect on tomato, eggplant, pepper, tobacco, potato, siraitia grosvenorii and ginger bacterial wilt (ginger blast) can reach 70-92%.
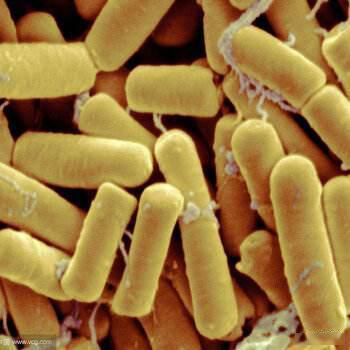
bacillus amyloliquefaciens
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has strong anti disease and antibacterial effects. It can secrete more than ten kinds of lipopeptide antibiotics and other antifungal active substances, mainly including antifungal proteins, surfactants, etc. These secretions interact with the lipid membrane of the virus through physical and chemical interactions, damaging the membrane structure and leading to the release of harmful bacterial intracellular solutes, ultimately causing cell death. It can effectively inhibit the activity of plant pathogenic fungi and has strong antibacterial effects. It can also inhibit the germination of nuclear disc fungi and inhibit their hyphal growth.
It can effectively inhibit or alleviate various plant diseases such as wheat sheath blight, cotton wilt, cotton red rot, cotton wilt, cucumber gray mold and disease, rapeseed and celery rot, rice blast, pepper wilt, yam root rot, apple anthracnose, ring rot, rot, brown spot, etc.
The concentrated powder of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens can rapidly reproduce and colonize in soil after application, effectively repelling and preventing plant pathogens from infecting plants; Simultaneously secreting extracellular metabolites to directly kill or inhibit the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens adsorbs onto the bacterial body of the pathogen, producing dissolved substances that dissolve the mycelium and cell wall, causing the bacterial body to break, disintegrate, perforate, and deform, playing a dissolving role; It can induce the plant's own disease resistance potential to enhance its disease resistance, promote the secretion of growth stimulating hormones by the plant itself, thereby promoting plant growth and reproduction, increasing yield and income.
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has a significant degradation effect on butachlor. The higher the initial mass concentration of butachlor, the higher its degradation rate and efficiency. Under alkaline conditions, the degradation rate of butachlor is significantly higher than under acidic conditions; The addition of humic acid can not only adsorb butachlor, but also promote bacterial microbial degradation of butachlor and affect the microbial degradation products of butachlor.
Bacillus megaterium
Phosphorus removal has a good effect on degrading organic phosphorus in soil
1. Improve the soil micro ecological environment.
2. Plants have increased tissue cell wall thickening, fibrosis, and lignification. And it forms a double silica layer of keratin outside the epidermal layer, forming a barrier to prevent bacterial invasion.
3. By converting ineffective phosphorus into available phosphorus, the absorption rate of phosphorus in soil can be effectively improved.
bacillus licheniformis
Disease resistance and killing of harmful bacteria
1. Effectively prevent diseases such as enteritis and gill rot in aquatic animals.
2. Decompose toxic and harmful substances in aquaculture ponds to purify water quality.
3. It has strong activity of protease, lipase, and amylase, promoting the degradation of nutrients in feed and enabling aquatic animals to absorb and utilize feed more fully.
4. Stimulate the development of immune organs in aquatic animals and enhance the body's immunity
5. It produces bioactive substances and has a unique biological oxygen scavenging mechanism, which can inhibit the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria.
Methylotrophic Bacillus subtilis
1. The metabolites (antifungal active lipopeptides) produced by methylotrophic Bacillus subtilis have strong antibacterial activity against plant fungal diseases, and have significant control effects on cucumber, tomato gray mold, late blight, cotton yellow wilt disease, apple tree rot disease, etc. It can also prevent and control citrus tree ulcer disease, cucumber bacterial leaf spot disease, rice bacterial leaf spot disease, etc.
2. Methylotrophic Bacillus produces aminopeptidases and acts as a PGPR (Plant Rhizosphere Promoter) to promote plant growth.
Cereus
1. Competitive effect
By competing for sites between endophytic and pathogenic bacteria to obtain nutrients, the occurrence of plant diseases can be suppressed. The pathway and mode of entry of Bacillus into the plant body are basically similar to that of pathogenic bacteria. After entering the host, Bacillus preferentially occupies the invasion point of pathogenic bacteria and competes with them for nutrients.
2. Antagonistic effect
Endophytic bacteria produce antibacterial substances through assimilation to inhibit the growth of pathogens or directly kill pathogens. Bacillus subtilis can secrete various antagonistic substances against fungi and bacteria (a novel antifungal cyclic peptide APS), which have a wide antibacterial spectrum and long-lasting inhibition. These substances have significant inhibitory effects on the spore germination and hyphal growth of pathogenic fungi.
3. Inducing plant resistance
(1) Bacillus can induce host plants to develop some physical structural resistance, depositing a large amount of woody and phenolic substances in the areas where the pathogen attempts to invade, thickening the cell walls of these areas and effectively preventing the invasion of the pathogen.
(2) Bacillus can also induce physiological and biochemical changes in host plants, accumulate related proteins, and produce hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes (such as chitinase, beta-1.3 glucanase, peroxidase) to inhibit the growth of pathogens.
(3) Bacillus cereus can secrete superoxide dismutase (SOD), which makes plants resistant to pathogens.
trichoderma harzianum
1. Competitive effect: Trichoderma harzianum rapidly grows around the roots and leaves of plants, occupying surface sites and preventing pathogenic fungi from contacting the roots and leaf surfaces, thereby protecting the roots and leaves from infection by the aforementioned pathogens.
2. Heavy parasitism: During the interaction between Trichoderma harzianum and pathogenic fungi, the host hyphae secrete metabolites that cause Trichoderma harzianum to grow towards the host fungus. The host is recognized by the Trichoderma harzianum parasite and a parasitic relationship is established. After recognizing the host fungus, Trichoderma harzianum mycelium grows parallel and helically along the host hyphae, and produces attached cellular branches that adsorb onto the host hyphae. By secreting extracellular enzymes to dissolve the cell wall, it penetrates the host hyphae, absorbs nutrients, and then kills the pathogen.
3. Antibiotic action: Trichoderma harzianum secretes some antibiotics that can inhibit the growth and colonization of pathogens, reducing their harm.
4. Plant growth regulation: Trichoderma harzianum colonizes plant roots and produces compounds that stimulate plant growth, improve the microenvironment of roots, enhance plant growth and disease resistance, and increase crop yield and income.
5. Inducing plant resistance and initiating plant defense responses
Trichoderma harzianum metabolizes to produce xylanase, and plants exhibit significant defense responses under the action of xylanase. K+, H+, Ca2+ion channels are opened to synthesize ethylene and accumulate PR proteins. The production of chitinase and β -1,3-glucanase by Trichoderma harzianum plays an important role in combating plant pathogenic fungi. Trichoderma harzianum triggers plant defense responses, leading to the production and accumulation of phenolic compounds and lignin related to disease resistance in plants. The protease produced simultaneously can degrade pathogenic bacteria that digest plant cell walls, directly inhibiting their germination, inactivating their enzymes, and preventing them from invading plant cells.
paecilomyces lilacinus
1. Promote plant growth
Penicillium purpureum can produce rich derivatives, such as indole-3-acetic acid products. Its most significant physiological effect is to promote plant root and plant growth at low concentrations. Penicillium purpureum colonization in plant roots not only significantly inhibits nematode infection, but also promotes the growth of plant nutrient organs, as well as seed germination and growth.
2. Generate multiple functional enzymes
Penicillium purpureum produces abundant chitinase, which has a degrading effect on chitin. It can promote the hatching of nematode eggs and increase the parasitic rate of Penicillium on nematodes. In addition, it also produces cell lytic enzymes, glucanases, and silk proteases to promote cell division.
3. Degradation effect
Penicillium purpureum can promote the dissolution of insoluble phosphates, with a solubilization effect of 30% for Penicillium purpureum and 20% to 40% for nematodes.
4. Penicillium pseudomallei promotes the decomposition of many chemical polymers, such as pesticides and tannery wastewater, and has environmental benefits.
5. After contact with nematode egg sacs, the biocontrol fungal hyphae surround the entire egg in a viscous matrix, and the hyphae become thicker at the ends. Due to the activity of exogenous metabolites and fungal chitinase, the surface layer of the egg shell ruptures, followed by fungal invasion and replacement. Simultaneously secreting toxins to have a toxic effect on nematodes.
bacillus thuringiensis
Insecticide (including root knot nematodes, most effective against arthropods such as Lepidoptera)
Bacillus thuringiensis can be used as a low toxicity insecticide derived from microorganisms, mainly for stomach toxicity. This bacterium can produce two types of toxins, namely endotoxins (accompanied by cell crystals) and exotoxins, which cause pests to stop feeding and eventually die due to hunger, cell wall rupture, blood damage, and neurotoxicity; Exotoxins act slowly and have a significant effect during molting and metamorphosis, which are the peak periods of RNA (ribonucleic acid) synthesis. Exotoxins can inhibit DNA dependent RNA polymerase. The effect of this medicine is slow, and it takes about 2 days for pests to take effect after feeding, with a duration of about 1 day. Therefore, it should be used 2-3 days earlier than conventional chemical agents, and the effect is better when used during the early stage of pests. Safe for fish and bees, but highly toxic for silkworms.
Bacillus thuringiensis preparations mainly have good control effects on the larvae of some Lepidoptera pests, and can be used to prevent and control cabbage caterpillars, rice corn borers, pine caterpillars, tobacco green worms, corn borers, cotton bollworms, rice leaf rollers, moths, and ground tigers. The insecticidal principle is that after being ingested by pests, Bacillus thuringiensis parasitizes in the host's midgut and grows and reproduces in a suitable alkaline environment. The crystal toxin is hydrolyzed by proteases in the insect's intestinal tract, forming smaller toxic subunits that act on the upper skin cells of the midgut, causing intestinal paralysis, perforation, paralysis, and cessation of feeding. Subsequently, Bacillus thuringiensis entered the bloodstream and propagated, causing leukorrhea and resulting in the death of the parasite
Bacillus thuringiensis can only fully exert its function when the temperature is high (above 20 ℃), so its application effect is best from July to September; It is generally advisable to apply pesticides 2-3 days earlier than using chemical pesticides.
Bacillus mucilaginosus
Dissolve phosphorus, release potassium, fix nitrogen, secrete various enzymes, enhance crop resistance to some diseases
Bacillus subtilis can produce carbonic anhydrase, which has a certain effect on the fixation of carbon dioxide. At present, these bacteria are the best strains for use as biofertilizers to promote the conversion of ineffective phosphorus and potassium in soil, increase soil phosphorus and potassium supply, and improve crop yield. Their Bacillus subtilis has a strong ability to hydrolyze phosphorus, potassium, and silicon.
1. Decomposing potassium and silicon from minerals such as feldspar and mica, as well as phosphorus from apatite, has the functions of dissolving phosphorus, releasing potassium, and fixing nitrogen. At the same time, it can produce organic acids, amino acids, polysaccharides, hormones, and other substances that are beneficial for plant absorption and utilization during growth and reproduction.
2. After propagating in the soil, plant growth stimulants and various enzymes are secreted to enhance crop resistance to certain diseases; It also inhibits the growth of other pathogens.
3. The potassium inside the bacterial cells is released after death and can be absorbed and utilized by plants. As an important functional bacterium in microbial fertilizers, it can increase the content of available potassium and phosphorus in soil, improve crop yield and quality, and have multiple effects.
 2025-05-17
2025-05-17